Küresel kentleşmenin hızlanmasıyla birlikte, belediye inşaatları çok sayıda yeraltı boru hattının döşenmesini ve değiştirilmesini gerektirmektedir. Özellikle günümüzün hızla gelişen Çin'inde, kent sakinleri güçlü bir çevre bilincine sahiptir ve projelerin yolları kazmayı, otlaklara ve çevredeki peyzajlara zarar vermeyi vb. içermemesini talep etmektedir.
İnşaat sırasında, su boruları zamanla hasar gördüğünde veya aşındığında, boru hattı uzmanları borunun her bölümüne çok dikkat ederek kazı yapmak ve onarmak zorundadır. Boruların bu şekilde onarılması sadece maliyetli ve emek yoğun olmakla kalmaz, aynı zamanda çevreye de zarar verir. Artık modern kazısız boru hattı teknolojisi sayesinde, eski boru hatlarını uygun maliyetli ve sürdürülebilir yöntemler kullanarak tam hizmet verebilir hale getirmek mümkün.

Kazısız teknoloji nedir?
Kazısız teknoloji, bir dizi yeraltı boru döşeme yöntemini ifade eder. Bunlar, yüzeyde hendek kazmadan çeşitli yeraltı boru hatlarının döşenmesi, değiştirilmesi ve onarılmasına yönelik yeni inşaat teknolojileridir. Yüzeyde yalnızca minimum kazı yaparak (genellikle giriş ve çıkışta küçük alanlı kazılara atıfta bulunarak) bunu başarmak için yönlü sondaj ve yönlendirme gibi yöntemlerin kullanılmasını içerirler.
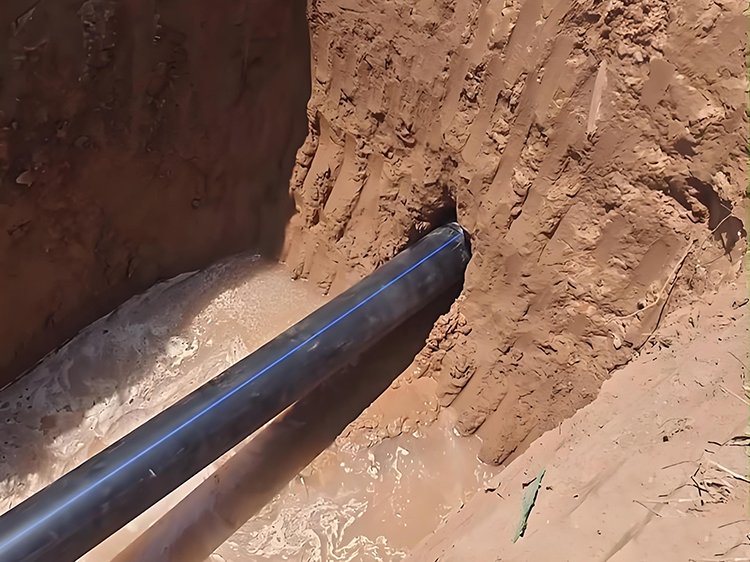

Geleneksel kanal açma yöntemleriyle karşılaştırıldığında kazısız teknoloji, trafikte minimum kesinti, çevreye zarar vermeme, daha kısa inşaat süresi ve önemli sosyal faydalar gibi avantajlar sunar. Yol trafiği, çimenler ve bahçeler, ticari faaliyetler ve diğer faaliyetlerle etkileşimi en aza indirebilir.
Kazısız boru döşeme teknolojisi geniş bir uygulama yelpazesine sahiptir. İşlek otoyollar, demiryolları, binalar, nehirler ve kentsel alanlarda boru hattı döşemek için kullanılabilir. Su temini, drenaj, elektrik, iletişim ve gaz alanlarında yeni boru hatlarının inşasında ve eski boru hatlarının onarımında yaygın olarak kullanılmaktadır. Ayrıca kültürel kalıntıların ve eski binaların korunması için de kullanılabilir.
Kazısız teknolojinin pe borularda uygulanması
PE boru, kazısız inşaatta en yaygın kullanılan boru türüdür ve aşağıdaki dört yaygın kazısız inşaat yönteminde yaygın olarak kullanılmaktadır ve Çin'de de başarıyla uygulanmıştır.
Yatay yönlü sondaj boru döşeme
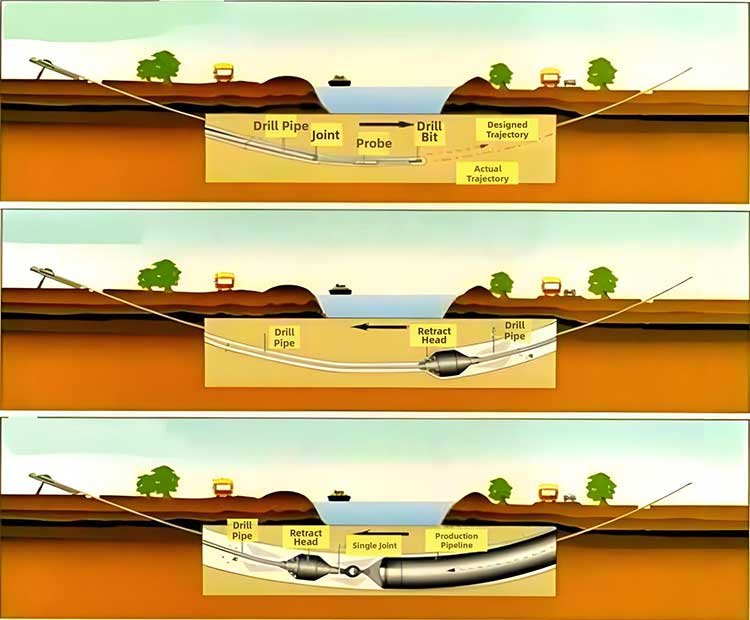
Yönlü sondaj, bir çalışma kuyusu kazmaya gerek kalmadan yeraltı boru hatlarının hızlı bir şekilde kurulmasını sağlayan bir sondaj yöntemidir. Ana özelliği, önceden tasarlanmış bir boru hattı güzergahına göre, kama şeklinde bir matkap ucuyla donatılmış bir sondaj çubuğunun zemine çakılması ve ardından hedefe ulaşılana kadar yeraltı engellerinin etrafında önceden belirlenmiş bir yönü takip etmesidir. Daha sonra matkap ucu çıkarılır ve yerine özel boyutta ve tipte bir geri dönüş raybası yerleştirilir, bu rayba sondaj deliğini gerekli çapa genişletirken aynı anda matkap çubuğunu geri çeker. Döşenecek boru hattı aynı anda sondaj deliği girişine geri çekilerek yeni döşenen boru hattının yetersiz alan veya sondaj kesiklerinden kaynaklanan sürtünme nedeniyle hasar görmemesi sağlanır.
Günümüzde telekomünikasyon boru hatları, enerji boru hatları, doğal gaz boru hatları ve su tedarik boru hatlarında yaygın olarak kullanılmaktadır.
Yönlü sondajın avantajları:
(1) Bir çalışma kuyusu kazmaya gerek yoktur; 100 mm ila 1000 mm arasında değişen çaplarda çeşitli malzemelerden boru hatları döşemek için uygundur;
(2) Maksimum torka ve benzersiz bir tasarıma sahip bir sondaj sistemi çoğu jeolojik koşulun üstesinden gelebilir;
(3) Özel olarak tasarlanmış kama şeklindeki matkap ucu, engellerden kaçınmak için delme yönünün kolayca ayarlanmasını sağlar;
(4) Yönlendirme ve konumlandırma sistemi 30,5 m'ye kadar derinlikleri ölçebilir ve doğru inşaat rotaları sağlar;
(5) Hızlı inşaat; tek bir sondaj işlemi 600 metreye kadar bir mesafeye ulaşabilir;
(6) HDPE katı duvarlı borular başta olmak üzere çeşitli malzemelerden kazısız boru hatlarının döşenmesi için uygundur.
Eski boruların değiştirilmesi için boru çatlatma yöntemi

Bu yöntem, eski borunun parçalanmasını ve çevresindeki toprağa sıkıştırılmasını içerir. Ardından, orijinal borunun bulunduğu yere yeni bir boru çekilir. Eski boruyu kırmak için genellikle pnömatik (yüksek basınçlı hava) veya statik (hidrolik) boru kırma sistemi kullanılır. Kırılan uçtan sonra bir PE boru bağlanır. Eski boru tamamen kırıldığında, yeni HDPE boru da döşenir ve böylece eski borunun yerini alır.
Bu yöntemin avantajı, yeni borunun çapının değiştirilen eski boruya eşit veya hatta daha büyük olabilmesidir. Dezavantajı ise yeni boru, çevresindeki kırık eski borunun içine yerleştirildiği için kaçınılmaz olarak hasar görmesidir. Bu nedenle, boru malzemesi son derece iyi hasar direncine, aşınma direncine ve çatlama direncine sahip olmalıdır.
Eski boruların entübasyon yöntemiyle onarılması
Bu teknoloji, eski bir borunun içine plastik bir astar yerleştirilmesini içerir. Astarın dış çapının eski borunun iç duvarına tam olarak oturup oturmadığına bağlı olarak iki kategoriye ayrılabilir: “Slip-lining” ve “fitting liner”.”
Slip-lining yöntemi, dış çapı eski borunun iç çapından biraz daha küçük olan yeni bir polietilen borunun onarılacak eski borunun içine yerleştirilmesini içerir. Yeni ve eski borular arasındaki boşluk harç enjekte edilerek kapatılabilir.
Fitting liner yöntemi, dış çapı eski borunun iç çapına eşit olan yeni bir plastik linerın “çap küçültme” veya “içe katlama” gibi yöntemlerle eski boruya yerleştirilmesini içerir. Ardından, astarın doğal olarak şeklini geri kazanmasına izin verilir veya basınçlandırma ve ısıtma yoluyla orijinal şekline getirilerek eski borunun iç duvarına tam oturması sağlanır. Bağlantı astarı iç basıncı eski boru ile paylaşabilir.
Bu yöntem yalnızca büyük çaplı boruların onarımı için uygundur ve borunun akış kesit alanı kaybı nispeten büyüktür.
Pnömatik mızraklı boru döşeme
Kazısız boru döşeme, darbe yoluyla mızrak şeklinde bir matkap ucu kullanılarak gerçekleştirilir. Tahrik mekanizması çoğunlukla pnömatiktir (ancak hidrolik de kullanılabilir) ve genellikle pnömatik mızraklı boru döşeme yöntemi olarak adlandırılır. Pnömatik mızrak, çekiç ile toprak arasındaki sürtünme tarafından desteklenir ve ileri doğru itilir, darbe altında sıkıştırma yoluyla bir delik oluşturur. Döşenecek boru hattı pnömatik çekice bağlanır ve çekiç toprakta ilerledikçe döşenir. Alternatif olarak, PE boru pnömatik mızrak delme işlemini tamamladıktan sonra deliğe geri çekilebilir.
Bu yöntem basit, verimli ve düşük maliyetlidir. Boru döşeme uzunlukları genellikle 40 m'dir ve boru çapları 40 ila 200 mm arasında değişir. Çeşitli toprak tipleri için uygundur. En yeni aletler, çakıllı topraklarda kullanıma izin veren pistonlu bir keski başlığı içerir.
Kazısız teknolojinin temel avantajları
Zamandan ve kesintiden tasarruf edin
Geleneksel kazı işlemleri diğer boru döşeme veya onarım yöntemlerine göre daha uzun sürer. Yolların altında hendek kazmak, trafik kesintisini en aza indirmek için işin gece tamamlanması gerektiği anlamına gelir. Kazısız kurulum ve onarım, trafiğin yoğun olduğu dönemlerde bile hasarlı boruların daha hızlı onarılmasını sağlar ve yolların altından tünel açılmasına izin verir.
Maliyet tasarrufu: Kazısız teknoloji genellikle en uygun maliyetli seçenektir çünkü büyük teknisyenlere, trafik yöneticilerine, ekskavatörlere, bahçıvanlara vb. olan ihtiyacı ortadan kaldırır. Kazısız yöntemler ayrıca ekipman ve alet gereksinimlerini en aza indirir ve işçilik maliyetlerinizi azaltır. Daha az rahatsız edici ve çevre dostu bir alternatif: Kazısız teknoloji çok az kazı gerektirir ve bu da çevredeki peyzaja minimum zarar verir. Kazısız kurulumlar ayrıca duvarların yıkılması veya yeniden yüzey kaplaması gibi yapısal değişiklikler gerektirmez, bu da boru altyapısının kurulumunu mümkün olduğunca kolaylaştırır.
HDPE boruların daha dayanıklı hale getirilmesi
HDPE borular standart PVC, çelik veya beton borulara göre daha fazla esneklik, hasar direnci ve sızdırmazlık sunar. HDPE boruları kazısız teknoloji ile kullanmak size benzersiz boru dayanıklılığı sağlar.
Sonuç
Kazısız PE boru teknolojisi, minimum inşaat rahatsızlığı, düşük çevresel etki, kısa inşaat süresi ve yüksek maliyet etkinliği gibi avantajlara sahiptir. Polietilen (PE) boru hatlarının döşenmesi veya onarımı için yönlü sondaj, eski boruları değiştirmek için boru patlatma ve eski boruları onarmak için boru yerleştirme gibi kazısız tekniklerin kullanılması, yalnızca geleneksel “açık kazı” inşaatının neden olduğu trafik, ticaret ve konut yaşamındaki kesintileri etkili bir şekilde önlemekle kalmaz, aynı zamanda boru hattı ağ sisteminin genel sızdırmazlığını ve dayanıklılığını da önemli ölçüde artırır.